The Planets
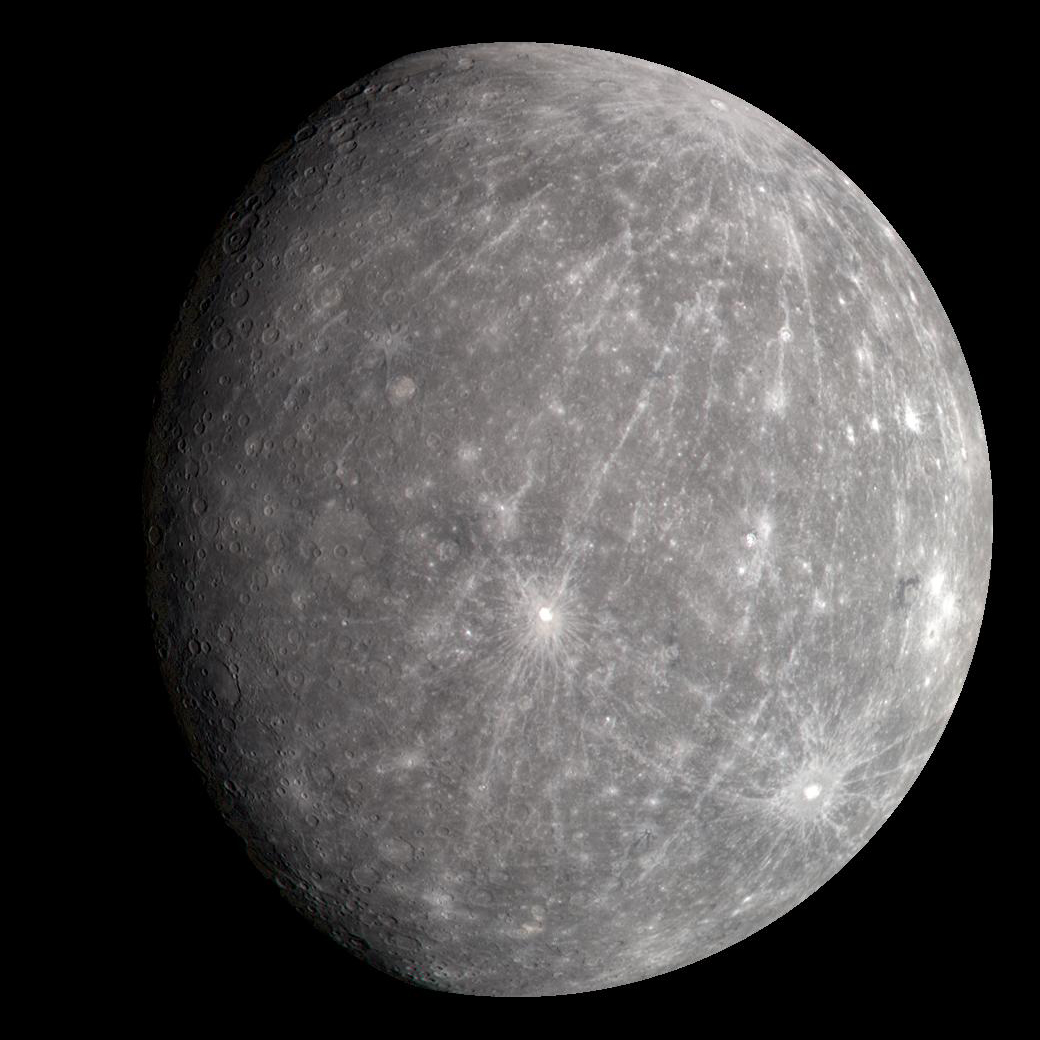

Mercury is the smallest planet in the Solar System and the closest to the Sun. Its orbit around the Sun takes 87.97 Earth days, the shortest of all the Sun's planets. It is named after the Roman god Mercurius (Mercury), god of commerce, messenger of the gods, and mediator between gods and mortals, corresponding to the Greek god Hermes (Ἑρμῆς). Like Venus, Mercury orbits the Sun within Earth's orbit as an inferior planet, and its apparent distance from the Sun as viewed from Earth never exceeds 28°.
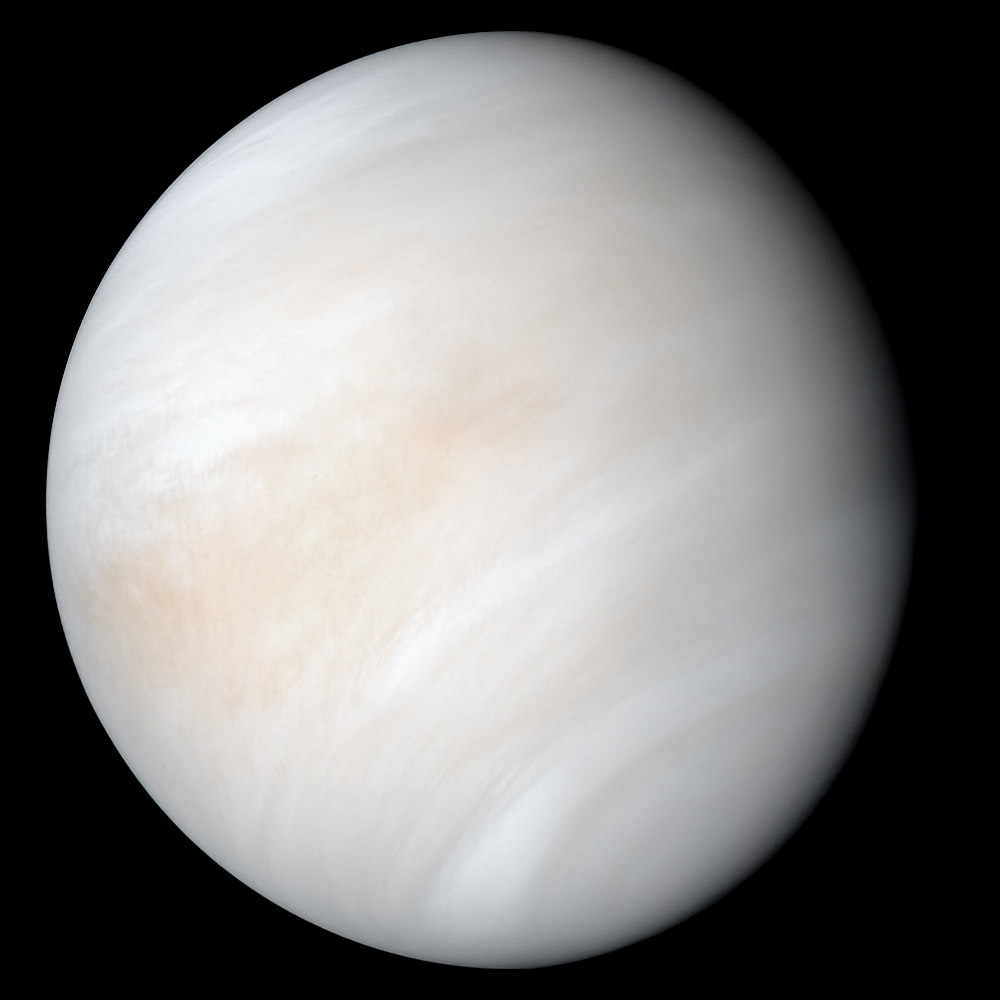

Venus is the second planet from the Sun and is named after the Roman goddess of love and beauty. As the brightest natural object in Earth's night sky after the Moon, Venus can cast shadows and can be visible to the naked eye in broad daylight. Venus's orbit is smaller than that of Earth, but its maximal elongation is 47°; thus, at latitudes with a day-night cycle, it is most readily visible for up to a few hours following the start of sunset or before sunrise. At times, it has been seen in a completely dark sky.

Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surface is made up of the ocean, dwarfing Earth's polar ice, lakes, and rivers. The remaining 29% of Earth's surface is land, consisting of continents and islands. Earth's surface layer is formed of several slowly moving tectonic plates, interacting to produce mountain ranges, volcanoes, and earthquakes. Earth's liquid outer core generates the magnetic field that shapes Earth's magnetosphere, deflecting destructive solar winds. Earth is orbited by one permanent natural satellite, the Moon, which orbits Earth at 380,000 km (1.3 light seconds) and is roughly a quarter as wide as Earth. The Moon always faces the Earth with the same side through tidal locking and causes tides, stabilizes Earth's axis, and gradually slows its rotation.
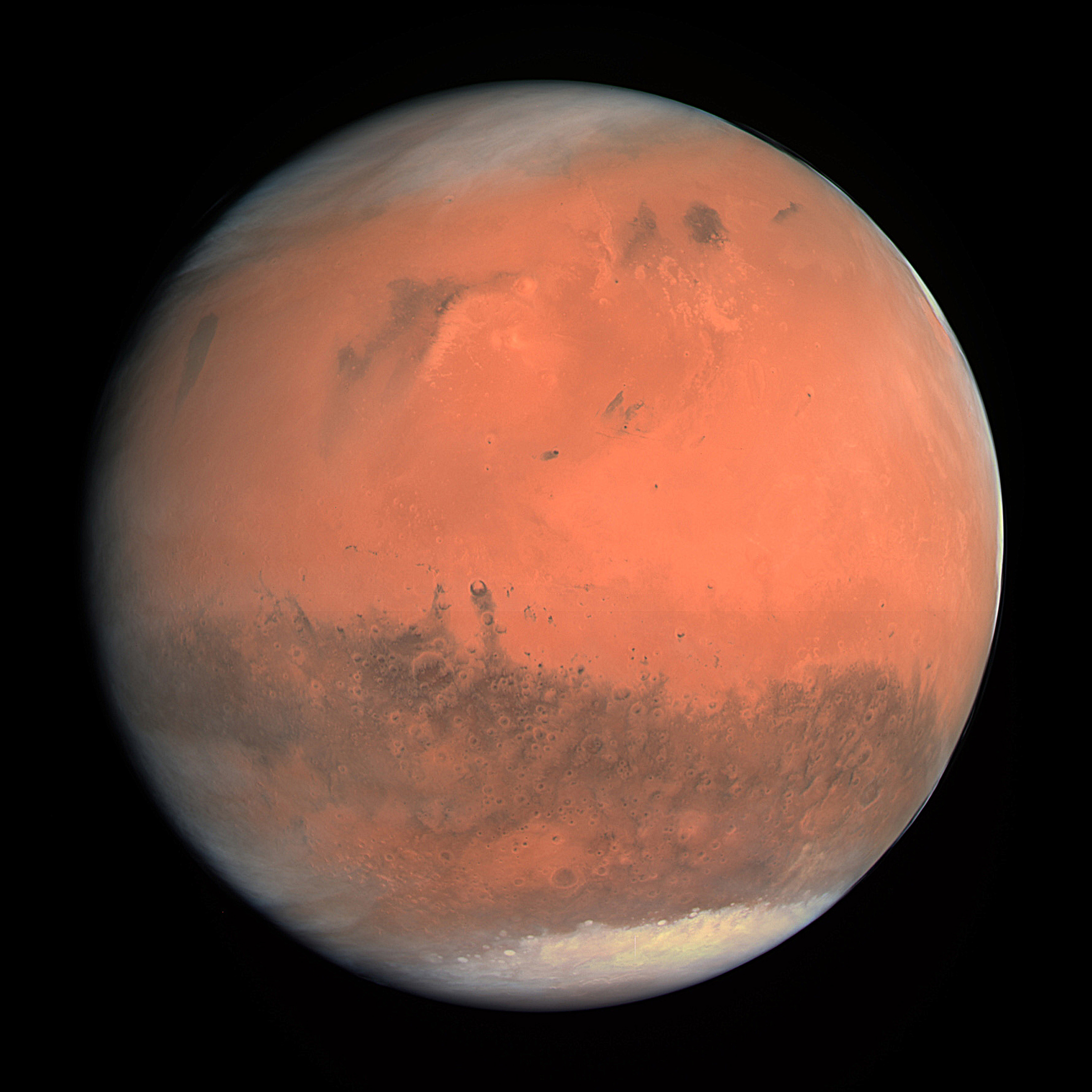

Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, being larger than only Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmosphere, and has a crust primarily composed of elements similar to Earth's crust, as well as a core made of iron and nickel. Mars has surface features such as impact craters, valleys, dunes, and polar ice caps. It has two small and irregularly shaped moons: Phobos and Deimos.
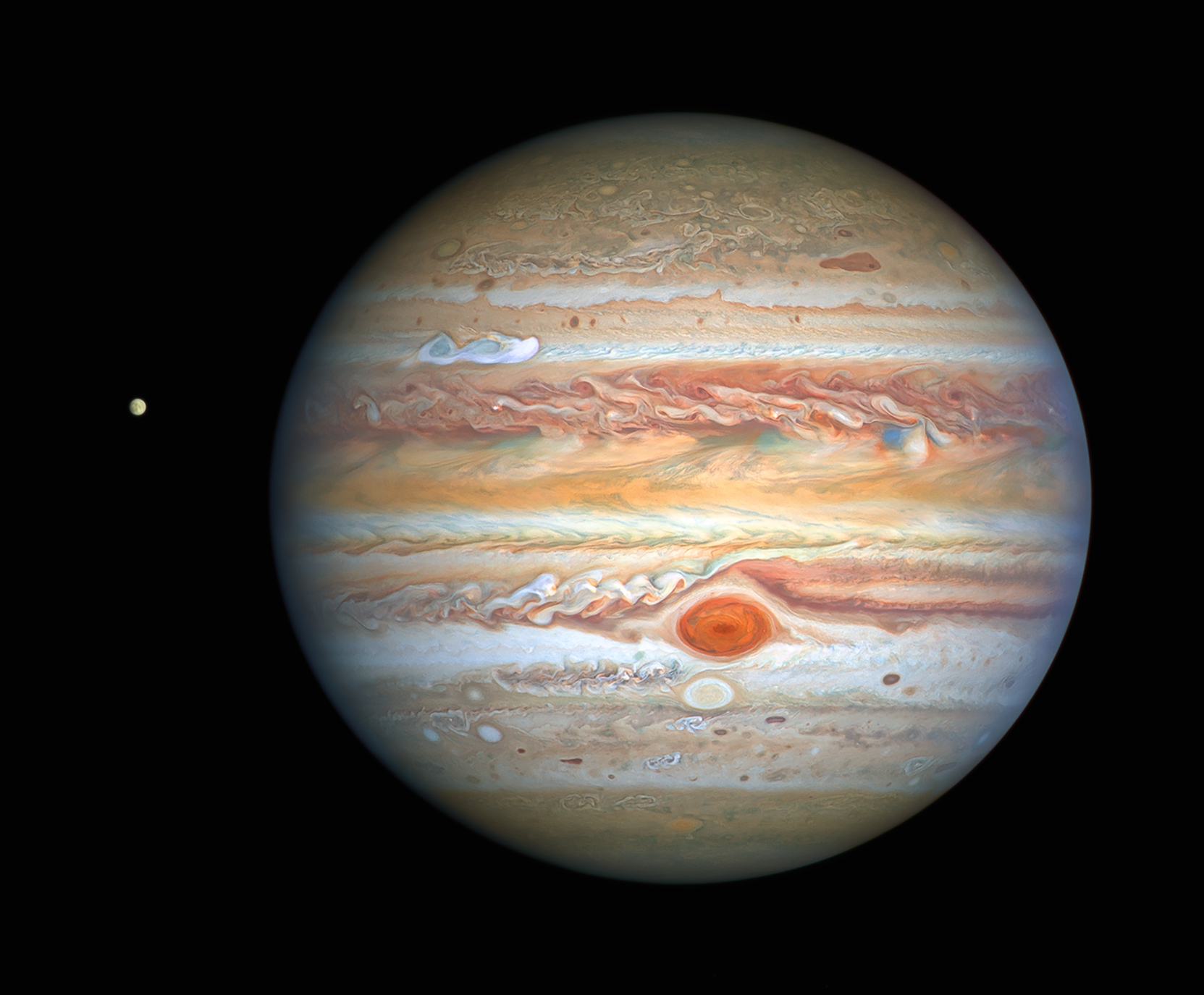
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandth the mass of the Sun. Jupiter is the third brightest natural object in the Earth's night sky after the Moon and Venus, and it has been observed since prehistoric times. It was named after the Roman god Jupiter, the king of the gods.
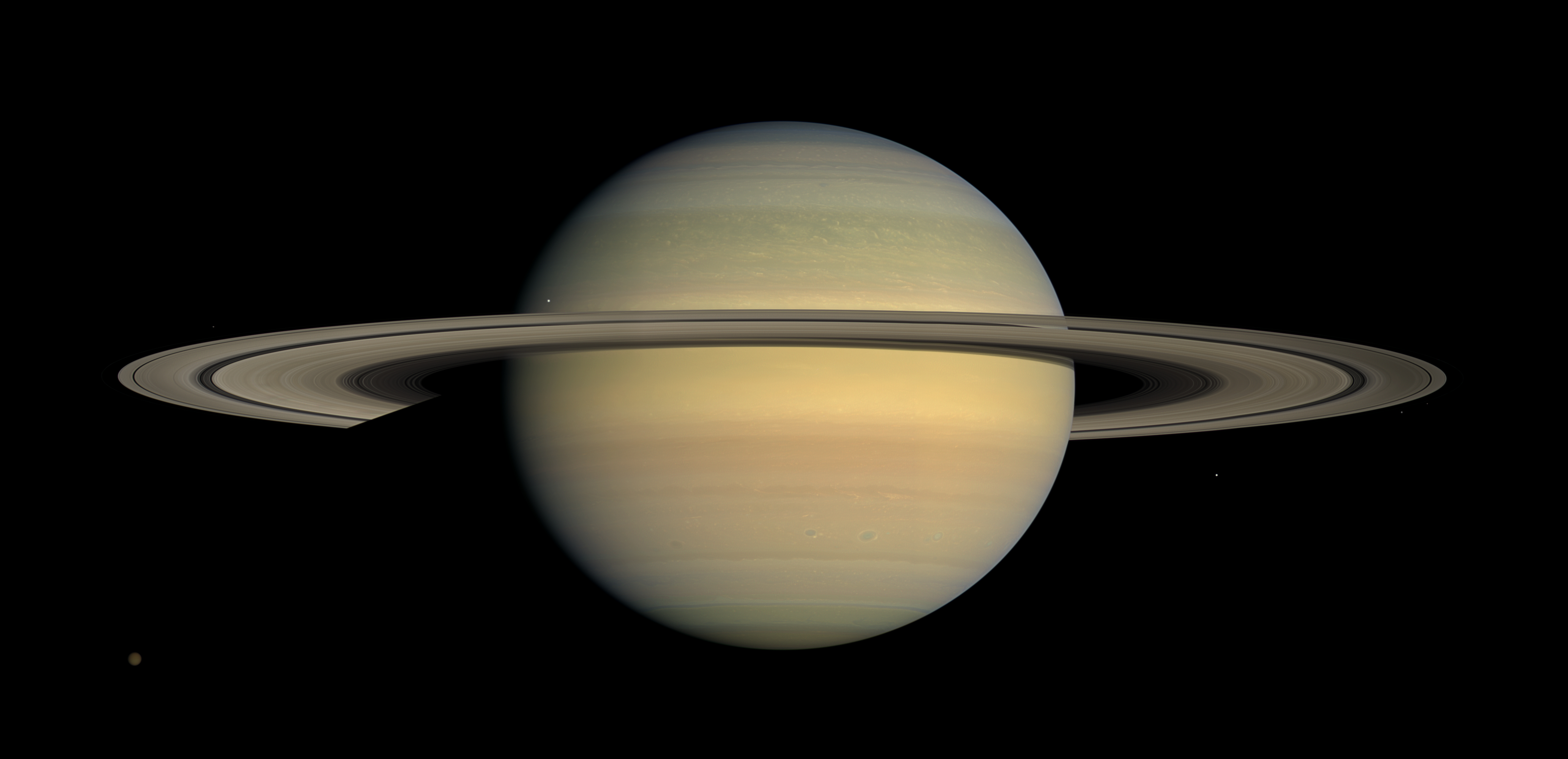
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; however, with its larger volume, Saturn is over 95 times more massive.
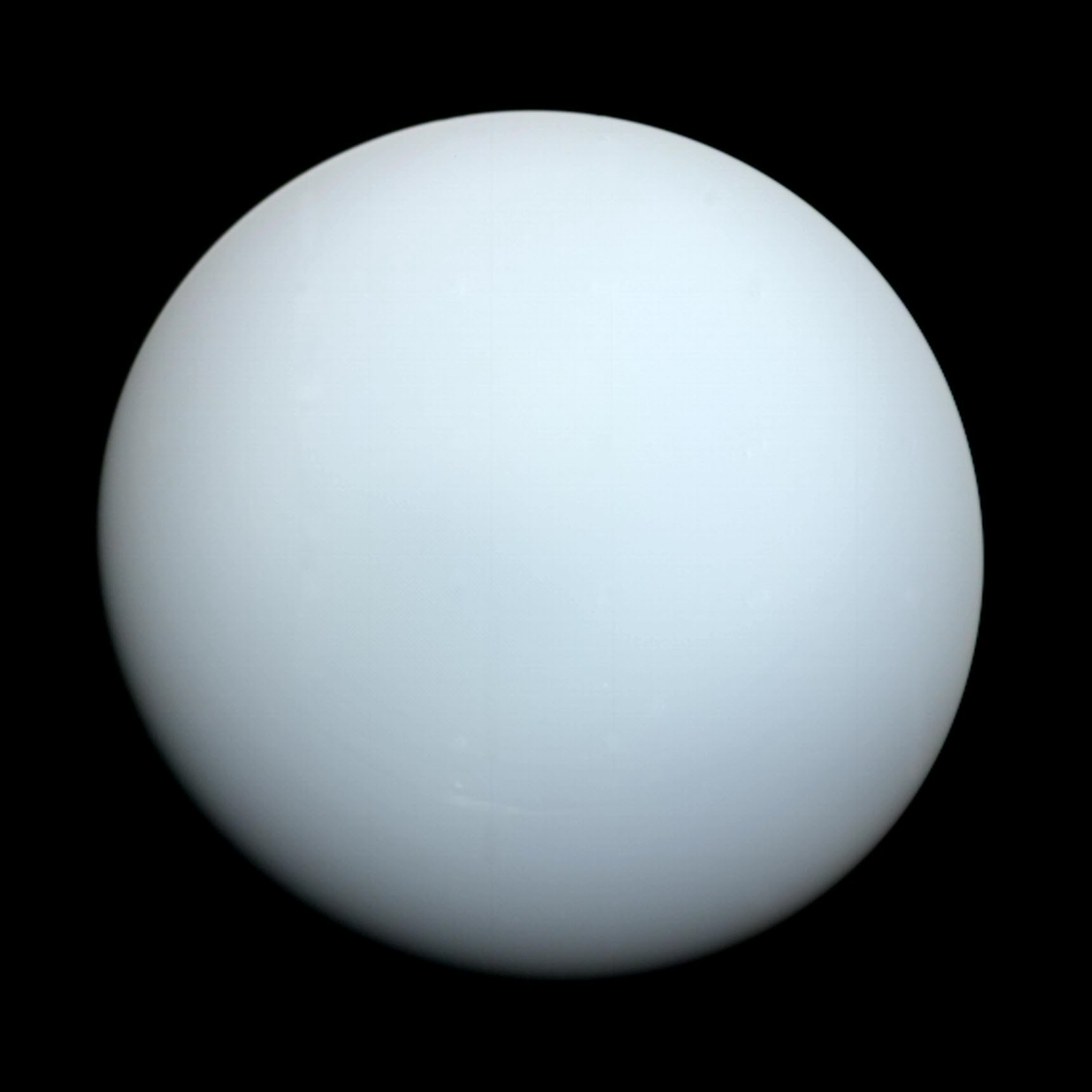

Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. Its name is a reference to the Greek god of the sky, Uranus (Caelus), who, according to Greek mythology, was the great-grandfather of Ares (Mars), grandfather of Zeus (Jupiter) and father of Cronus (Saturn). It has the third-largest planetary radius and fourth-largest planetary mass in the Solar System. Uranus is similar in composition to Neptune, and both have bulk chemical compositions which differ from that of the larger gas giants Jupiter and Saturn. For this reason, scientists often classify Uranus and Neptune as "ice giants" to distinguish them from the other giant planets.
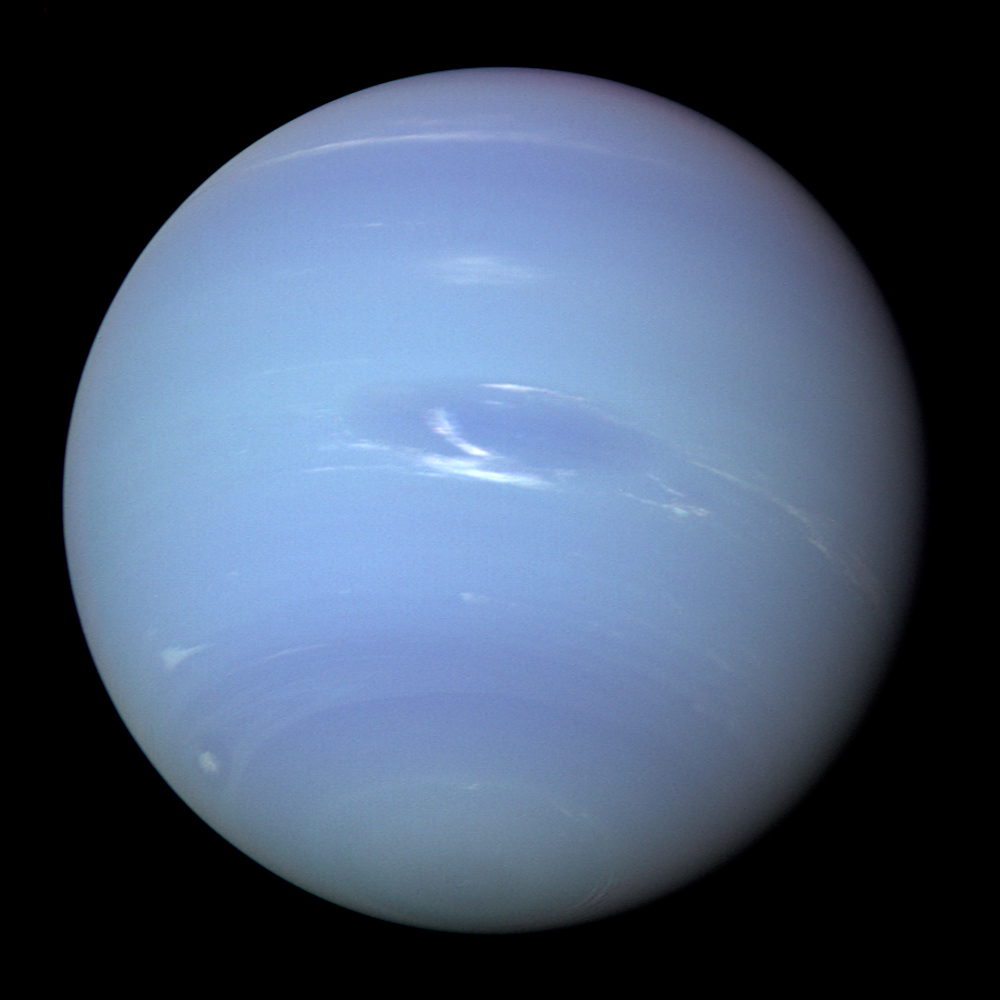
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known solar planet. In the Solar System, it is the fourth-largest planet by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times the mass of Earth, and slightly more massive than its near-twin Uranus. Neptune is denser and physically smaller than Uranus because its greater mass causes more gravitational compression of its atmosphere. It is referred to as one of the solar system's two ice giant planets (the other one being Uranus).

Pluto is a dwarf planet in the Kuiper belt, a ring of bodies beyond the orbit of Neptune. In 1930, it was the first object discovered in the Kuiper belt, when it was declared the ninth planet from the Sun. Beginning in the 1990s, following the discovery of several objects of similar size in the Kuiper belt including the dwarf planet Eris, and the scattered disc, Pluto's status as a planet was questioned. In 2006 the International Astronomical Union (IAU) formally re-defined the term planet, reclassifying Pluto as a dwarf planet.